Annually, approximately one-eighth of all fatalities in the United States can be partially attributed to heart failure complications. Among the most prevalent indicators of acute heart failure is fluid accumulation in the lungs, medically termed pulmonary edema.
The precise quantification of excess fluid typically guides physicians' therapeutic decisions, yet accurately determining these levels remains challenging. Medical practitioners must often depend on subtle radiographic features in X-ray images, which can result in inconsistent diagnoses and varying treatment approaches.
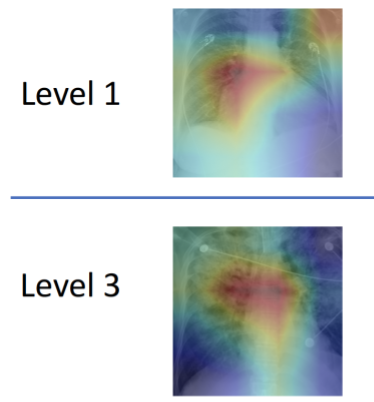
To address this diagnostic complexity, a research team spearheaded by experts at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) has engineered an innovative machine learning system capable of analyzing chest X-rays to assess edema severity on a four-tier scale (0 representing healthy conditions, while 3 indicates extremely severe cases). This diagnostic tool accurately identified the correct severity level in over 50% of cases, with an impressive 90% accuracy rate for the most critical level 3 cases.
In collaboration with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Philips, the research team aims to implement this AI-powered diagnostic tool into BIDMC's emergency department procedures by autumn.
"This initiative is designed to enhance clinical workflows by supplying healthcare professionals with additional data points that can inform diagnostic decisions while facilitating retrospective medical analyses," explains Ruizhi Liao, a doctoral student who co-led the research alongside fellow PhD student Geeticka Chauhan and MIT professors Polina Golland and Peter Szolovits.
The research team emphasizes that improved edema diagnostics would enable medical practitioners to better manage not only acute cardiac conditions but also other health complications such as sepsis and renal failure, which demonstrate strong correlations with pulmonary edema.
As part of a separate scholarly publication, Liao and his research team utilized an existing public dataset of X-ray images and created new severity annotations that were validated through consensus among four radiology specialists. Liao anticipates that these standardized labels could establish a universal benchmark for evaluating future machine learning advancements in this field.
A distinctive feature of this system is its training methodology, which involved not only processing over 300,000 X-ray images but also analyzing the corresponding radiological reports. The team was notably surprised by their system's remarkable success in utilizing these reports, despite the fact that most lacked specific severity level annotations.
"By establishing correlations between imaging data and their corresponding textual reports, this approach introduces a novel methodology for automated report generation based on image-driven findings," observes Tanveer Syeda-Mahmood, a researcher unaffiliated with the project who serves as chief scientist for IBM's Medical Sieve Radiology Grand Challenge. "Nevertheless, additional experimentation would be necessary to broaden its applicability to other medical findings and their detailed descriptors."
Chauhan's contributions focused on enabling the system to interpret the textual content of radiological reports, which frequently consisted of merely one or two sentences. Given that different radiologists employ diverse writing styles and terminology, the researchers had to develop linguistic guidelines and substitution protocols to ensure consistent data analysis across various reports. This challenge was compounded by the technical complexity of designing a model capable of jointly training image and text representations in a meaningful way.
"Our model can transform both visual and textual data into condensed numerical representations from which clinical interpretations can be derived," Chauhan explains. "We trained it to minimize the discrepancy between X-ray image representations and the corresponding radiology report text, leveraging the reports to enhance image interpretation accuracy."
Furthermore, the team's system demonstrates "explainability" by highlighting which sections of reports and specific areas of X-ray images contribute to its predictions. Chauhan expresses optimism that future developments in this domain will yield more detailed image-text correlations at a granular level, enabling clinicians to develop comprehensive taxonomies of images, reports, disease labels, and relevant anatomical regions.
"These correlations will prove invaluable for enhancing search capabilities within extensive databases of X-ray images and reports, thereby increasing the effectiveness of retrospective medical analyses," Chauhan notes.
The research paper was co-authored by Chauhan, Golland, Liao, Szolovits, MIT Assistant Professor Jacob Andreas, Professor William Wells of Brigham and Women's Hospital, Xin Wang of Philips, and Seth Berkowitz and Steven Horng of BIDMC. The findings will be presented virtually on October 5 at the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI).
This research initiative received partial funding from the MIT Deshpande Center for Technological Innovation, the MIT Lincoln Lab, the National Institutes of Health, Philips, Takeda, and the Wistron Corporation.